一步步实现 Promises/A+ 规范 -- 系列一
2019年06月04日预计阅读需要 10 分钟
一步步实现 Promises/A+ 规范 -- 系列
Promises/A+ 规范
一些术语

翻译:
promise是一个遵循本规范、并拥有then方法的对象或函数thenable是一个定义了then方法的对象或函数value是JavaScript中任意一种合法值(包括undefined,thenable以及promise)exception是一个使用throw语句抛出的值reason是一个指示了promise为何被拒绝(rejected)的值
Promises/A+ 规范要求
状态要求

翻译:
一个 Promise 必须是以下三种状态之一:等待态(pending)、完成态(fulfilled)或拒绝态(rejected)
- 处于
pending状态,可以转化为fulfilled或rejected - 处于
fulfilled状态,不能转换其它状态;且必须有一个不可改变的value - 处于
rejected状态,不能转换其它状态;且必须又一个不可改变的reason
这里的“不可改变”指的是可通过 === 进行比较,对于引用变量的复杂深层对象属性,不作约束
根据上述要求,验证 Promise 代码如下:
// 验证代码一
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("success");
reject("fail");
});
console.log(promise);
// {status: 'resolved' value: 'success'}
// 状态不会由 resolved 变为 rejected初步实现 Promise 如下
// 实现代码一
const PENDING = "pending";
const RESOLVED = "resolved"; // fulfilled
const REJECTED = "rejected"; //rejected
class Promise {
// 构造函数接收一个执行器作为参数
constructor(executor) {
// promise 状态
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
const resolve = value => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.value = value;
this.status = RESOLVED;
}
};
const reject = reason => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.reason = reason;
this.status = REJECTED;
}
};
// 执行 执行器,并传入两个方法作为参数
executor(resolve, reject);
}
}
module.exports = Promise;executor 错误收集
执行如下代码:
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
throw new Error("error");
});
console.log(promise);
// {status: 'rejected', reason: 'error'}
// 即直接抛出错误,需要执行 reject因此需要修改实现
executor(resolve, reject);
// 改为
try {
executor(resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}then 方法要求 - 第 1 部分
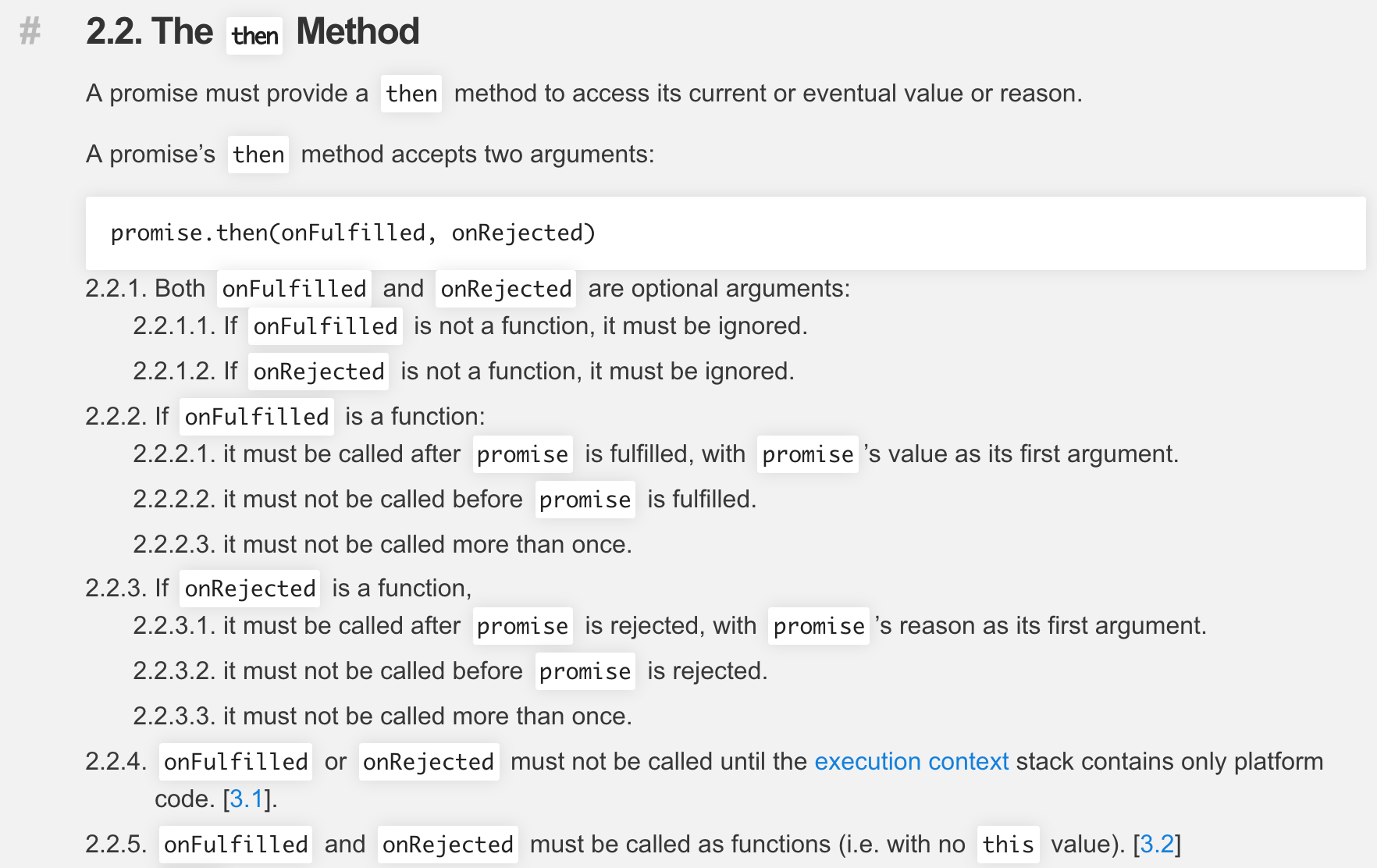
翻译:
一个 Promise 必须提供一个 then 方法,来访问其当前或最终的 value 或 reason
Promise 的 then 方法接受两个参数
promise.then(onFulfilled, onRejected);-
onFulfilled与onRejected都是可选参数- 如果
onFulfilled不是函数,必须将其忽略 - 如果
onRejected不是函数,必须将其忽略
- 如果
-
如果
onFulfilled是一个函数- 当
promise完成(fulfilled)后必须对其调用,并且promise最终的值(value)作为第一个参数 promise未完成(fulfilled)前,不能对其调用- 调用次数不可超过一次
- 当
-
如果
onRejected是一个函数- 当
promise被拒绝(rejected)后必须对其调用,并且promise最终的原因(reason)作为第一个参数 promise未被拒绝(rejected)前,不能对其调用- 调用次数不可超过一次
- 当
- 这句意思是只有在
Promise的执行器中调用了resolve或reject方法,才调用then方法中的onFulfilled或onRejected方法。可以看官网中的注释理解这条用途,就是为了保证then方法中的两个参数异步执行 onFulfilled和onRejected必须被作为函数调用,即没有this,严格模式下this为undefined,非严格模式为全局对象
第4条理解起来可能比较费解,用代码演示它解决的痛点,往下看
根据上述要求,验证 Promise 代码如下:
// 验证代码二
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("success");
}, 1000);
}).then(
res => {
console.log(res);
},
err => {
console.log(err);
}
);
// 延时 1s 打印 success实现 Promise 如下
不实现第4条代码:
// 实现代码二
const PENDING = "pending";
const RESOLVED = "resolved"; // fulfilled
const REJECTED = "rejected"; //rejected
class Promise {
// 构造函数接受一个执行器作为参数
constructor(executor) {
// promise 状态
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
// 成功回调数组
this.onFulfilledCallbacks = [];
// 失败回调数组
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
const resolve = value => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.value = value;
this.status = RESOLVED;
this.onFulfilledCallbacks.forEach(func => {
func(this.value);
});
}
};
const reject = reason => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.reason = reason;
this.status = REJECTED;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach(func => {
func(this.reason);
});
}
};
try {
// 执行 执行器,并传入两个方法作为参数
executor(resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
}
// then 方法接受两个方法作为参数
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
// 根据状态执行不同的回调
if (this.status === RESOLVED) {
onFulfilled(this.value);
} else if (this.status === REJECTED) {
onRejected(this.reason);
} else if (this.status === PENDING) {
// pending 状态将方法存入对应的数组
if (typeof onFulfilled === "function") {
this.onFulfilledCallbacks.push(onFulfilled);
}
if (typeof onRejected === "function") {
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(onRejected);
}
}
}
}
module.exports = Promise;用 实现代码二 测试 验证代码二 时,测试结果符合规范。但面对同步、异步两种调用时,表现形式是不一样的,如 验证代码三 和 验证代码四 的输出结果不同
// 验证代码三
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log(1);
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('success');
}, 300)
}).then((res) => {
console.log(3);
}, (err) => {
console.log(err);
})
console.log(2);
// 输出 1 2 3 符合规范
// --------------
// 验证代码四
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log(1);
resolve('success');
}).then((res) => {
console.log(3);
}, (err) => {
console.log(err);
})
console.log(2);
// 输出 1 3 2 不符合规范因此需要将 resolve 和 reject 两个方法改为异步执行,同时 then 方法中的状态判断也就不需要了,因为 then 肯定先于 resolve 和 reject 执行,则状态一定是 pending,整体修改如下
// resolve 方法修改
const resolve = value => {
// 实现异步执行 then 方法中的两个参数 onFulfilled onRejected
// 对应第4条要求
const timer = setTimeout(() => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
clearTimeout(timer);
this.value = value;
this.status = RESOLVED;
this.onFulfilledCallbacks.forEach(func => {
func(this.value);
});
}
}, 0);
};
// reject 方法修改
const reject = reason => {
// 实现异步执行 then 方法中的两个参数 onFulfilled onRejected
// 对应第4条要求
const timer = setTimeout(() => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
clearTimeout(timer);
this.reason = reason;
this.status = REJECTED;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach(func => {
func(this.reason);
});
}
}, 0);
};
// then 方法简化
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
if (typeof onFulfilled === "function") {
this.onFulfilledCallbacks.push(onFulfilled);
}
if (typeof onRejected === "function") {
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(onRejected);
}
}这样对于 验证代码三 和 验证代码四 就统一了结果输出,并且符合规范
本篇实现了规范中对状态的要求,以及部分 then 方法的要求。在下一篇文章中将实现 then 链的逻辑